Chamaecrista fasciculata
 |
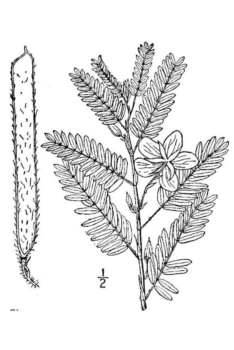 |
Photo courtesy Renee Brecht |
Britton & Brown |
| Botanical name: | Chamaecrista fasciculata (Michx.) Greene var. fasciculata |
| Common name: | Partridge pea or sleeping plant |
| Synonomy: | Cassia
brachiata (Pollard) J.F. Macbr. Cassia chamaecrista L. Cassia fasciculata Michx. Cassia fasciculata Michx. var. brachiata (Pollard) Pullen ex Isely Cassia fasciculata Michx. var. depressa (Pollard) J.F. Macbr. Cassia fasciculata Michx. var. ferrisiae (Britt. ex Britt. & Rose) Turner Cassia fasciculata Michx. var. puberula (Greene) J.F. Macbr. Cassia fasciculata Michx. var. rostrata (Woot. & Standl.) B.L. Turner Cassia fasciculata Michx. var. robusta (Pollard) J.F. Macbr. Cassia fasciculata Michx. var. tracyi (Pollard) J.F. Macbr. Cassia mississippiensis Pollard Cassia robusta (Pollard) Pollard Cassia rostrata (Woot. & Standl.) Tidestrom ex Tidestrom & Kittell Chamaecrista brachiata Pollard Chamaecrista depressa (Pollard) Greene Chamaecrista littoralis Pollard Chamaecrista mississippiensis (Pollard) Pollard ex Heller Chamaecrista robusta (Pollard) Pollard ex Heller Chamaecrista rostrata Woot. & Standl. Chamaecrista tracyi Pollard |
| Group: | dicot |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Growth type: | forb/herb |
| Duration: | annual |
| Origin: | native |
| Plant height: | 1 to 4 feet tall (usually 1 to 2 feet), branching freely, with short hairs. |
| Foliage: | Alternate, evenly pinnate compound, 1 to 4 inches long. Each leaf with 6 to 15 pairs of linear-oblong leaflets. The leaflets are smooth but have sparsely hairy margins and either blunt or pointed tips. |
| Flower: | Yellow, showy, 5 petals, the upper 4 petals with a reddish spot at the base, the lower petal is larger. 2 - 7 flowered racemes. Flowers are clustered in the axils of the leaves. |
| Flowering time: | Flowers late July to mid-Septmeber; fruits in early September too late October. Seed a flat pod (legume) 1 to 2.5 inches long, containing 4 to 20 seeds. |
| Habitat: | Sandy or rocky soils; disturbed areas, prairies, open woods, waste ground, and along roads. |
| Range in New Jersey: | Characteristic of Middle district, but with tendency to become weedy, spreading over railroad embankments and in cultivated ground. |
| Heritage ranking, if any: | n/a |
| Distribution: | 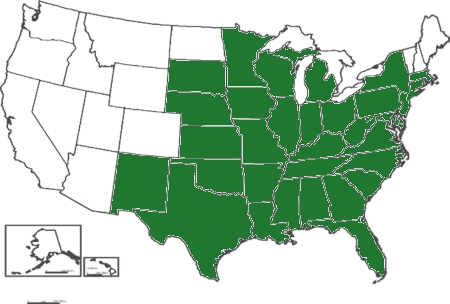 |
| Misc. | This
plant is a member of the pea family, but its flower petals do not have
the characteristic "pea" shape. It may be that it it One of the petals
curves completely back to cover the center of the flower as if to aid
with pollinators. It may be attempting to become more "pea-like", or
perhaps just the opposite, trying to become less "pea-like". The leaves are touch-sensitive. They will fold when disturbed. Upland game birds and songbirds eat the seeds, and deer and cattle will consume the foliage. Partridge pea can be mildly poisonous to livestock when consumed in large quantities, but deer seem unaffected. USDA information: The seed is one of the major food items of northern bobwhite and quail because it remains in sound condition throughout the winter and early spring. Erosion control: The plant can be used along road banks and stream banks to control erosion. Recreation and beautification: The flowers of this plant can be used to beautify areas where wildflowers are planted. Partridge pea usually reseeds but will gradually disappear without regular maintenance. Light disking to remove weeds, small brush, and old sod is necessary for healthy plantings or natural stands. In areas where prescribed burning is permitted, controlled fire is an excellent method for controlling unwanted vegetation. Fire or disking should be done in late winter for best results. Weeds can also be controlled during the growing season by mowing over the top of the partridge pea. Chamaecrista, Greek chamai (dwarf) and crista (crest); fasciculata, in bunches or bundles. |